State Tax Guidelines for Freelancers: Staying Above Board
Understanding state taxes as a freelancer can feel like navigating a maze. Did you know that taxes for freelancers differ significantly from those of regular employees? This guide will simplify the process and demystify the complexities of state, federal and self-employment taxes for independent professionals.
Keep reading to unravel the secrets of seamless tax filing!
Key Takeaways
- Freelancers have different tax obligations compared to regular employees, including federal income taxes, state income taxes, self-employment taxes, local tax requirements, sales tax, and side hustle taxes.
- Choosing the right business structure is crucial for freelancers as it determines how their taxes are filed. Options include sole proprietorship, LLC, or S corporation.
- Freelancers need to estimate and pay quarterly taxes throughout the year to avoid penalties or interest charges. Accurate record keeping of income and expenses is essential for making these estimations.
- Taking advantage of deductions and deductibles can help freelancers reduce taxable income and lower their overall tax liabilities. Common deductions include business expenses and home office expenses if used solely for work purposes.
Taxes for Freelancers: The Basics
Freelancers need to understand the difference between employee and freelancer taxes, as well as the types of taxes they must pay, including federal, state, and local taxes, along with sales tax.
Understand the difference between employee and freelancer taxes
Freelancers and traditional employees both pay taxes, but the process differs significantly for each. For starters, most employers handle tax deductions for their workers automatically; freelancers, however, need to manage this themselves.
A freelancer is essentially self-employed and must take on the responsibility of paying federal income tax as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes that would typically be split between an employee and employer.
Furthermore, freelancers could face state-specific tax obligations which vary from one location to another. Finally, freelancers have unique opportunities for business-related deductions that aren’t available to regular employees – a potential boon come tax season if properly tracked throughout the year.
Understanding these differences can help make sense of your taxation responsibilities as a freelancer.
Types of taxes freelancers must pay
Freelancers bear the responsibility of several tax obligations. Their unique employment status necessitates a specific type of tax reporting and payment. Here are the types of taxes that freelancers must pay:
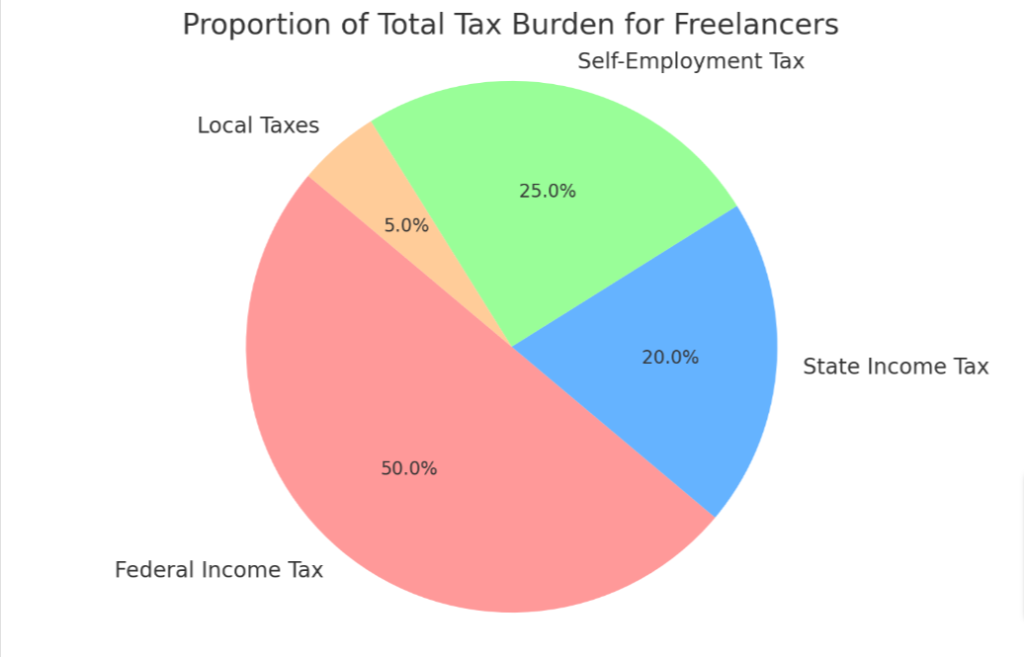
- Federal Income Taxes: The government levies this tax on the financial income generated by all entities within their jurisdiction.
- State Income Taxes: These taxes are imposed by your state on income earned within its boundaries.
- Self-Employment Taxes: Freelancers owe self-employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Local Tax Requirements: Depending on the city or county you live in, you may also have to pay local income taxes.
- Sales Tax: If you sell goods or certain services, you might need to collect sales tax and pass it onto the state.
- Side Hustle Taxes: Freelancers sometimes get entangled in multiple jobs to earn income; such earnings also come under freelance tax liabilities.
Federal, state, and local taxes
Freelancers must manage numerous tax obligations across different governing bodies. Federal taxes are a substantial portion of these, requiring attention to income tax, self-employment tax as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes.
State taxes for freelancers vary widely depending on your location, with some states imposing hefty rates while others have no state income tax at all. Similar to states, local taxes can differ dramatically based on city or municipality regulations – often adding sales tax or business license fees to the mix.
Navigating this multitude of responsibilities is critical for every freelancer wanting to stay in good standing with federal, state and local authorities.
Sales tax
Sales tax is another important aspect of taxes that freelancers need to understand. When you sell products or services, you may be required to collect sales tax from your customers and remit it to the appropriate taxing authority.
This can vary depending on the state where you live and operate your business. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific sales tax regulations in your state and comply with them accordingly.
By understanding and fulfilling your sales tax obligations, you can ensure legal compliance and avoid any penalties or fines.
How to File Taxes as a Freelancer
Learn how to navigate the complexities of filing taxes as a freelancer, including understanding your business structure, estimating quarterly taxes, keeping records, and maximizing deductions.
Don’t miss out on this essential information for freelancers!
Understanding your business structure
Choosing the right business structure is essential for freelancers as it determines how their taxes are filed. As a freelancer, you have several options to consider, such as operating as a sole proprietorship, forming an LLC (Limited Liability Company), or even establishing an S corporation.
Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability protection, tax obligations, and administrative requirements. It’s crucial to understand these differences so that you can select the most appropriate structure for your freelance business.
By choosing the right business structure, you’ll ensure that you comply with state tax regulations and maximize your tax deductions while maintaining flexibility and simplicity in managing your freelance income.
Estimated quarterly taxes
Freelancers are responsible for paying their own taxes, and this includes estimated quarterly taxes. These payments are made to the IRS throughout the year, typically in April, June, September, and January.
Freelancers must estimate their income for the year and calculate how much they owe in taxes each quarter. This ensures that they stay on track with their tax obligations and avoid any penalties or interest charges from underpayment.
It’s important for freelancers to keep accurate records of their income and expenses so they can make an accurate estimation of their tax liability each quarter.
Record keeping
Keeping accurate records is crucial for freelancers when it comes to filing taxes. As a freelancer, you need to maintain detailed records of your income and expenses throughout the year.
This includes invoices, receipts, bank statements, and any other financial documents related to your freelance work. By keeping organized records, you can easily calculate your tax obligations and ensure that you are reporting the correct amount of income.
Additionally, record keeping allows you to claim deductions accurately and avoid any potential audits or penalties from tax authorities. Stay on top of your record keeping to make tax time less stressful and more straightforward for yourself as a freelancer.
Deductions and deductibles
Freelancers have the advantage of being eligible for various deductions and deductibles when filing their taxes. These deductions can help reduce taxable income, ultimately lowering the amount owed in taxes.
Some common deductions for freelancers include business expenses such as office supplies, travel expenses, and marketing costs. Additionally, freelancers may be able to deduct a portion of their home office expenses if they use a designated space solely for work purposes.
It’s important to keep detailed records and receipts of these expenses to ensure accurate reporting during tax season. By taking advantage of available deductions and deductibles, freelancers can maximize their savings and potentially lower their overall tax liabilities.
Best Accounting and Tax Software for Freelancers
To effectively manage their taxes, freelancers can benefit from using accounting and tax software that is specifically designed for their needs. These software options automate calculations, track expenses, generate reports, and even help with tax filing.
Some popular choices include QuickBooks Self-Employed, FreshBooks, Wave Accounting, and TurboTax Self-Employed.
Importance of staying on top of tax obligations
Staying on top of your tax obligations is crucial for freelancers. By ensuring you fulfill your tax responsibilities, you can avoid penalties and legal issues. It is essential to keep accurate records, calculate and pay estimated quarterly taxes, and stay organized with your finances.
By using reliable accounting and tax software, you can simplify the process of managing your taxes. Seeking help from a tax professional or advisor can also provide valuable guidance and ensure you are meeting all state-specific requirements.
Don’t overlook the importance of staying on top of your tax obligations as a freelancer to maintain financial stability and compliance with the law.
Recommended software for managing taxes
When it comes to managing your taxes as a freelancer, having the right software can make a big difference. Here are some recommended options for keeping track of your tax obligations:
- QuickBooks: This popular accounting software offers features specifically designed for freelancers. It allows you to track income and expenses, create invoices, and calculate estimated quarterly taxes.
- FreshBooks: Known for its user-friendly interface, FreshBooks is an excellent choice for freelancers who want a simple yet effective tax management solution. It enables you to easily organize expenses, generate reports, and even automate invoicing.
- Wave: Ideal for small business owners and freelancers alike, Wave provides comprehensive bookkeeping and accounting tools at no cost. From tracking income and expenses to generating financial statements, this software has got you covered.
- TurboTax Self-Employed: If you prefer an all-in-one tax solution, TurboTax Self-Employed is worth considering. It guides you through the process of reporting freelance income and claiming relevant deductions while ensuring accuracy and compliance.
- Expensify: Keeping track of receipts can be a hassle for freelancers. With Expensify, you can easily snap photos of your receipts using your smartphone and categorize them accordingly. The software also integrates with various accounting platforms.
Staying Organized and Ahead of Your Freelance Taxes
To stay on top of your freelance taxes, it’s important to establish good financial management habits. Keep track of all your income and expenses by maintaining organized records. Seek assistance from a tax professional to ensure you’re meeting all necessary obligations.
Stay proactive by making estimated quarterly tax payments and keeping up with any changes in state or local tax requirements. By staying organized and ahead of your freelance taxes, you can avoid potential issues down the road and ensure a smoother tax filing process.
Tips for managing and organizing finances
Here are some tips to help you manage and organize your finances as a freelancer:
- Keep separate bank accounts for business and personal expenses.
- Track your income and expenses using accounting software or a spreadsheet.
- Set aside money for taxes by calculating and saving a percentage of each payment you receive.
- Create a budget to control your spending and prioritize business investments.
- Save receipts and invoices to support deductions and expenses during tax season.
- Regularly review your financial statements, such as profit/loss reports, to gauge the health of your business.
- Consider automating payments and invoicing to save time and minimize errors.
- Stay on top of debt obligations and make timely payments to maintain a good credit score.
- Plan for future financial goals by setting up an emergency fund or retirement savings account.
Seeking help from a tax professional
If you’re feeling overwhelmed or unsure about filing your taxes as a freelancer, seeking help from a tax professional can provide valuable guidance. A tax professional specializes in understanding the intricacies of tax laws and regulations, and they can assist you in navigating the complexities of your freelance tax obligations.
They can help you identify potential deductions, ensure accurate reporting of your income, and minimize any risk of errors or audits. By consulting with a tax professional, you’ll have peace of mind knowing that your taxes are being handled correctly while freeing up time for you to focus on growing your freelance business.
How to pay taxes as a freelancer
Paying taxes as a freelancer is an important part of managing your business. Here are some steps to help you navigate the process:
- Determine your tax obligations based on your freelance income and business structure.
- Keep track of your income and expenses throughout the year for accurate reporting.
- Calculate your self – employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare.
- Check the tax regulations in your state to understand any specific requirements or deductions.
- File your taxes on time, either through self – filing or with the help of a tax professional.
- Pay any taxes owed by the due date to avoid penalties and interest.
Conclusion
Knowing the ins and outs of state taxes as a freelancer is crucial for managing your finances. From understanding different types of taxes to filing your taxes correctly, staying organized is key.
Take advantage of tax software and seek help from a professional if needed to ensure you stay on top of your state tax obligations as a freelancer.

