Tax Deductions Decoded: Maximizing Your Write-Offs
Everyone loves to save money, especially when it comes to taxes. Did you know that the average American misses out on around $5,000 in tax deductions each year? This blog post will guide you through understanding what tax deductions are and which ones you might be eligible for.
Stick around, your wallet will thank you!
Key Takeaways
- Tax deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe.
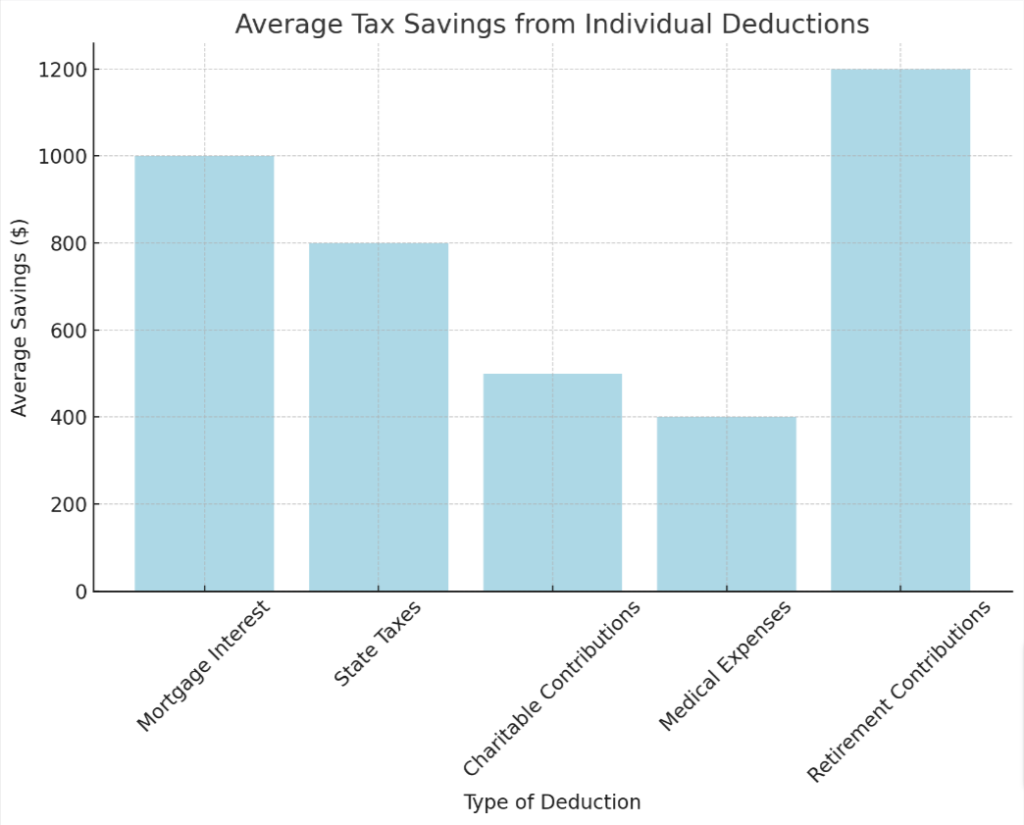
- Individual tax deductions include mortgage interest, state taxes, charitable contributions, medical expenses, and retirement contributions.
- Small business tax deductions include home office expenses, vehicle expenses, supplies and equipment costs, advertising and marketing costs, employee wages and benefits, travel expenses,and insurance premiums.
- Corporate tax deductions include business expenses,d epreciation of assets,research and development costs,and advertising and marketing expenses.
What are Tax Deductions?
A tax deduction is a type of expense that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows you to subtract from your taxable income. Essentially, they are expenditures that reduce your overall income, leading to a lower tax amount you owe at the end of the year.
Tax deductions come in many forms and vary based on whether it’s for an individual, small business, or corporation. These could include expenses like home mortgage interest for individuals or advertising costs for businesses.
Deductions might also stem from state taxes paid or charitable contributions made within the year. Understanding which expenditures are deductible can notably decrease your annual tax bill by reducing taxable income.
Types of Tax Deductions
There are three main types of tax deductions: individual tax deductions, small business tax deductions, and corporate tax deductions.
Individual tax deductions
Lowering your taxable income can be achieved through individual tax deductions. These are specific expenses that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows you to subtract from your total income. These include:
- Mortgage Interest: If you own a home and have a mortgage, you can deduct the interest paid on it.
- State taxes: You have the option to write off either your state income taxes or your state sales taxes.
- Charitable Contributions: Donations made to non-profit organizations could qualify for a deduction.
- Medical Expenses: Depending on your income level, some of your medical expenses may be deductible.
- Retirement Contributions: Money placed into a retirement account like an IRA often has tax benefits.
- Business Expenses: Some of the costs associated with running a small business from home could be deducted.
Small business tax deductions
Owning a small business comes with the benefit of several tax deductions. These expenses can significantly reduce your taxable income and increase your bottom line.
- Home Office Deduction: If you use part of your home exclusively for business, you may qualify for a home office deduction.
- Vehicle Expenses: When a personal vehicle is used for business purposes, expenses like gas, maintenance, insurance or even depreciation can be deducted.
- Supplies and Equipment: Purchase necessary items such as office supplies, furniture, computers or software solely for running your business? They are deductible!
- Advertising and Marketing Costs: This includes everything from business cards to billboards to digital advertising costs on social media platforms.
- Employee Wages and Benefits: Salaries, wages, bonuses or commissions paid to employees are all deductible expenses.
- Travel Expenses: Business travel costs like airfare, hotels, meals and transportation become tax deductions when related to your small business operations.
- Insurance Premiums: Any insurance premiums related directly to your trade or profession are tax-deductible.
- Utilities: If you have an office outside of your home, utility bills such as internet, phone bills, electricity are also deductible.
- Legal and Professional Fees: The cost of hiring professionals like accountants or attorneys can be written off.
- Education Expenses: Any education expense that helps maintain or improve skills required in your present job is acceptable as a tax deduction.
- Rent Expenses: Rent paid on buildings or other properties used in the course of doing business is another example of deductible expenses.
- Business Tax Preparation Fees: The cost incurred while preparing income tax returns specifically related to enterprise activities can be deducted from the taxable income.
Corporate tax deductions
Corporations can also take advantage of various tax deductions to reduce their taxable income. Here are some common corporate tax deductions:
- Business expenses: Corporations can deduct expenses related to running their business, such as rent, utilities, office supplies, and employee salaries.
- Depreciation: Companies can deduct a portion of the cost of their assets over time, reflecting the wear and tear or obsolescence of those assets.
- Research and development: Corporations can deduct expenses related to research and development activities aimed at improving or creating new products.
- Advertising and marketing: Companies can deduct costs associated with advertising and marketing campaigns to promote their goods or services.
- Travel expenses: When employees travel for business purposes, corporations can deduct expenses like airfare, lodging, meals, and transportation.
Common Tax Deductions
- Property taxes can be deducted from your taxable income.
- Mortgage interest is also deductible, helping homeowners save on their taxes.
- Charitable contributions can lower your tax bill while giving back to the community.
- Medical expenses that exceed a certain threshold are eligible for deduction.
- Retirement contributions can have tax benefits, allowing you to save for the future and reduce your taxable income.
- Business expenses such as advertising and legal fees can be deducted, saving small business owners money.
Property taxes
Property taxes are a type of tax deduction that homeowners can claim. These taxes are levied by local governments based on the assessed value of your property. By deducting your property taxes, you can reduce your taxable income and potentially lower the amount of federal income tax you owe.
To claim this deduction, make sure to keep track of how much you paid in property taxes throughout the year and include it when filing your tax return. It’s important to note that property tax deductions are only available if you itemize deductions instead of taking the standard deduction.
So, if you own a home and pay property taxes, be sure to take advantage of this potential tax savings opportunity.
Mortgage interest
Mortgage interest is one of the common tax deductions that homeowners can take advantage of. By deducting the amount of interest paid on their mortgage loans, homeowners can lower their taxable income and potentially reduce their overall tax liability.
This deduction applies to both primary residences and second homes, as long as the loan is secured by the property. It’s important to keep track of your annual mortgage interest statements (Form 1098) from your lender, as this will provide the necessary information for claiming this deduction when filing your taxes.
Remember to consult with a tax professional or use tax software to ensure you are eligible for this deduction and maximizing your potential savings.
Charitable contributions
Donating to charitable organizations can provide individuals with tax deductions. When you make a contribution to a qualified charity, you may be able to deduct that amount from your taxable income.
This means that the more you donate, the lower your overall tax liability may be. Whether it’s cash donations or donated items, keep track of your contributions and obtain receipts as proof for claiming these deductions on your tax return.
By giving back to causes you care about, not only are you making a difference but also potentially saving money on taxes.
Medical expenses
Medical expenses are a common tax deduction that can help reduce your taxable income. If you’ve incurred medical costs throughout the year, such as doctor’s visits, prescriptions, or hospital stays, you may be able to deduct them from your taxes.
Keep in mind that there are some limitations and restrictions on what qualifies as deductible medical expenses. It’s important to gather all necessary documentation and consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re taking full advantage of this deduction.
By claiming medical expenses on your tax return, you can potentially lower your overall tax bill and save money in the process.
Retirement contributions
Contributing to a retirement account can help lower your taxable income and potentially save you money on taxes. When you make contributions to a traditional IRA or 401(k), the amount you contribute is deducted from your taxable income for that year.
This means that if you contribute $5,000 to your retirement account, your taxable income will be reduced by $5,000. By lowering your taxable income, you may be able to reduce the amount of taxes owed and increase your tax refund.
If you qualify for a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k), keep in mind that these contributions are not tax-deductible. However, the earnings on these accounts are tax-free when withdrawn during retirement.
Business expenses (advertising, legal fees, etc.)
Business expenses such as advertising and legal fees can often be deducted from your taxable income. These deductions can help reduce the amount of taxes you owe, resulting in potential tax savings.
Keeping track of your business expenses throughout the year is important to ensure accuracy when claiming these deductions. By consulting with a tax professional or using accounting software, you can easily categorize and document these expenses to make tax time a breeze.
Limitations and Restrictions on Tax Deductions
Tax deductions are not a free pass to reduce your taxable income without any limits or restrictions. It’s important to be aware of the limitations and restrictions that come with claiming tax deductions.
Non-deductible expenses
Certain expenses are not eligible for tax deductions. Here are some common non-deductible expenses:
- Personal expenses such as rent, groceries, and clothing
- Political contributions or campaign expenses
- Penalties and fines imposed by government agencies
- Legal fees for personal matters like divorce or child custody battles
- Costs related to commuting to and from work, including gas, tolls, and parking fees
- Expenses for hobbies or activities not conducted for profit
- Club memberships or dues for recreational activities
Tricky tax deductions
Some tax deductions can be a bit tricky to navigate. Here are some common tricky deductions to be aware of:
- Home office deduction: If you work from home, you may be eligible for this deduction, but there are specific criteria that must be met.
- Unreimbursed employee expenses: While some job-related expenses can be deducted, there are limitations and requirements that must be met.
- Meal and entertainment expenses: Deducting these expenses requires careful record-keeping and adherence to IRS rules regarding what is considered a legitimate business expense.
- Education-related deductions: Certain education expenses may be deductible, but it’s important to understand the qualifications and limitations.
- Car expenses: If you use your car for business purposes, you may be able to deduct mileage or certain other vehicle-related expenses. However, strict documentation is necessary.
- Hobby losses: Deducting losses from a hobby can get complicated. The IRS has specific guidelines that determine whether an activity is considered a hobby or a business.
Know the difference between deductions and credits
Tax deductions and credits are both methods to reduce your tax liability, but they work in different ways. Deductions lower the amount of your taxable income, while credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe.
In simple terms, deductions decrease the pool of money that is subject to taxation, while credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax bill. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for maximizing your potential savings on taxes.
So make sure you know which expenses can be claimed as deductions and which ones qualify for tax credits when preparing your taxes.
Understanding the standard deduction
The standard deduction is a set amount that you can subtract from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe. It’s an alternative to itemizing your deductions. The standard deduction amount varies based on your filing status and changes each year.
It’s important to know the standard deduction because it affects how much you’ll pay in taxes. By understanding this deduction, you can determine whether it makes more sense for you to take the standard deduction or itemize your deductions when filing your taxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding tax deductions is crucial for maximizing your potential tax savings. By knowing what expenses you can write off, such as property taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and business expenses, you can reduce your taxable income.
Take advantage of the IRS allowed deductions and make sure to differentiate between deductions and credits. So start exploring the various deductions available to you and save money on your taxes today!

